Bandgap engineered monodisperse and stable mercury telluridequantum dots and their application for near-infrared photodetection†
Abstract
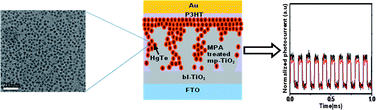
Bandgap-engineered monodisperse HgTe NCs of different sizes were synthesized by means of a facile temperature-control method, a non-aqueous and non-Te-gas process. The photo-physical properties of the synthesized NCs in a simple photovoltaic device were tested. It was shown that this cell is capable of processing signals up to the 100 kHz level below 3 dB and hence is suitable for use in NIR photodetection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...