The role of CH–π interaction in the charge transfer properties in tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium(iii)†
Abstract
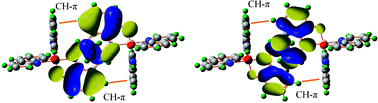
The charge mobility is a key property in many electro-optical materials, with charge transfer (CT) taking place in a solid matrix of molecules. Large intermolecular electronic interaction is one of the key factors for a good CT rate, which is dependent on both intra- and intermolecular structures. The connection of the molecular structure with the intermolecular CT property would facilitate the search for a new material with desirable CT property, but currently it is still quite limited by the lack of knowledge for intermolecular configurations. In the present work, we study factors influencing the intermolecular configurations, and subsequently the CT property, in tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato) aluminium(III) (AlQ3) from all currently available crystal structures. We found that there exists a pair of CH–π interactions in a good majority of the π–π stacked bimolecular configurations. Such CH–π and π–π interacting structures are also seen in the crystal structures of many other similar molecules. With both experimental and simulated structures, we show that the CH–π interaction stabilizes the bimolecular configurations, and drives the structure towards a region with a higher electron transfer coupling and lower hole transfer coupling. This effect likely affects the electron transport property of AlQ3, since it is consistent with recent experimental results, where AlQ3 analogs with their CH–π interaction blocked either require a higher operating voltage in light-emitting devices [Sapochak et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, 6300], or become bipolar in their charge mobilities [Liao et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 763]. CH–π interaction is commonly seen in aromatic molecules, which are frequently used as building blocks in molecules for electro-optical applications. Our work points out a possible way to enhance the desired CT property in the design of new materials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Aromaticity, electron delocalisation, and related molecular properties

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...