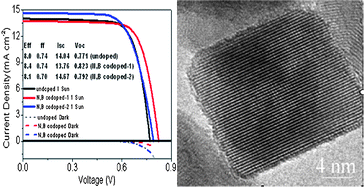
A facile process to fabricate highly crystalline mesoporous N,B codoped TiO2 is introduced. The N,B codoped TiO2 nanomaterial, which has controlled crystallographic phase, size and unique nanoshape, is successfully applied to an enhanced device for dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) with an open-circuit photovoltage of 0.823 V and yielding a high overall energy conversion of 8.4%. A DSC based on the N,B codoped TiO2 electrode shows a competitive photovoltaic performance compared with the undoped DSC, which is attributed to the ideal combination of superior energy band structure and retarded electron recombination from the unique N,B codoped TiO2 particle structure.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...