Spherical nanoporous LiCoPO4/C composites as high performance cathode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
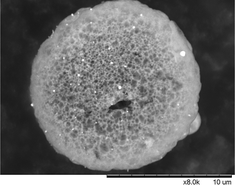
Spherical nanoporous LiCoPO4/C composite microparticles were synthesized from soluble precursors by
- This article is part of the themed collection: Advanced Materials for Lithium Batteries

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...