Ion hydration and structural properties of water in aqueous solutions at normal and supercooled conditions: a test of the structure making and breaking concept
Abstract
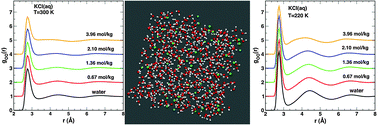
We study with the method of molecular dynamics simulation the structural properties of aqueous solutions of NaCl, KCl and KF salts at ambient conditions and upon supercooling at constant pressure. The calculations are performed at increasing concentration of the salt starting from c = 0.67 mol kg−1 up to 3.96 mol kg−1. We investigate the modifications of the hydration shells and the changes in the water structure induced by the presence of the ions. The oxygen–oxygen structure is strongly dependent on the ionic concentration while it is almost independent from the
- This article is part of the themed collection: Physics and chemistry of ice and water

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...