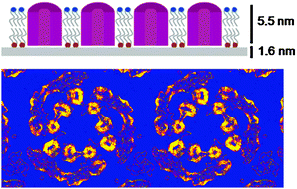
Ultrathin carbon nanomembranes (CNM) have been tested as supports for both cryogenic high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (cryo-EM) as well as atomic force microscopy (AFM) of biological specimens. Purple membrane (PM) from Halobacterium salinarum, a 2-D crystalline monolayer of bacteriorhodopsin (BR) and lipids, was used for this study. Due to their low thickness of just 1.6 nm CNM add virtually no phase contrast to the transmission pattern. This is an important advantage over commonly used amorphous carbon support films which become instable below a thickness of ∼20 nm. Moreover, the electrical conductivity of CNM can be tuned leading to conductive carbon nanomembranes (cCNM). cCNM support films were analyzed for the first time and were found to ideally meet all requirements of cryo-EM of insulating biological samples. A projection map of PM on cCNM at 4 Å resolution has been calculated which proves that the structural integrity of biological samples is preserved up to the high-resolution range. CNM have also proven to be suitable supports for AFM analysis of biological samples. PM on CNM was imaged at molecular resolution and single molecule force spectra were recorded which show no differences compared to force spectra of PM obtained with other substrates. This is the first demonstration of a support film material which meets the requirements of both, cryo-EM and AFM, thus enabling comparative structural studies of biomolecular samples with unchanged sample–substrate interactions. Beyond high-resolution cryo-EM of biological samples, cCNM are attractive new substrates for other biophysical techniques which require conductive supports, i.e. scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and electrostatic force microscopy (EFM).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...