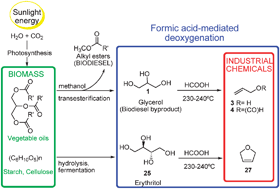
An efficient didehydroxylation method for the biomass-derived polyols glycerol and erythritol. Mechanistic studies of a formic acid-mediated deoxygenation†
Abstract
An efficient 1,2-deoxygenation method, involving an unexpected mechanism, was found for simple

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...