Synthesis and characterization of new red phosphors for white LED applications†
Abstract
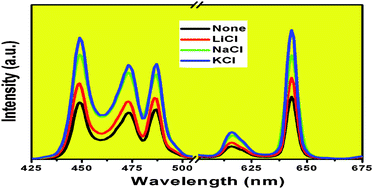
An efficient red phosphor, BaMoO4:Pr3+, has been fabricated by a convenient solid-state method. A strong red emission centered at 643 nm corresponding to the 3P0→3F2 transition of Pr3+ is observed under 430–500 nm excitation. In addition, improvement of the intensity of the red emission has been achieved by adding an alkali chloride to the BaMoO4:Pr3+ phosphor samples, this being explained by a charge compensation mechanism. The influence of the sintering temperature on the luminescence properties of the phosphors is also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...