Diethyl carbonate as a solvent for ruthenium catalysed C–H bond functionalisation†
Abstract
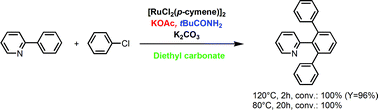
The ruthenium catalysed direct functionalisation of arene C–H bonds by aryl halides is reported. Reactions were performed in diethyl carbonate (DEC) instead of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...