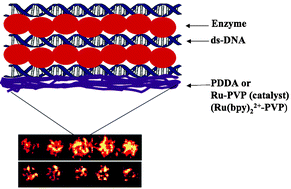
This feature article summarizes recent applications of ultrathin films of enzymes and DNA assembled layer-by-layer (LbL). Using examples mainly from our own research, we focus on systems developed for biocatalysis and biosensors for toxicity screening. Enzyme–poly(L-lysine) (PLL) films, especially when stabilized by crosslinking, can be used for biocatalysis at unprecedented high temperatures or in acidic or basic solutions on electrodes or sub-micron sized beads. Such films have bright prospects for chiral synthesis and biofuel cells. Excellent bioactivity and retention of enzyme structure in these films facilitates their use in detailed kinetic studies. Biosensors and arrays employing DNA–enzyme films show great promise in predicting genotoxicity of new drug and chemical product candidates. These devices combine metabolic biocatalysis, reactive metabolite–DNA reactions, and DNA damage detection. Catalytic voltammetry or electrochemiluminescence (ECL) can be used for high throughput arrays utilizing multiple LbL “spots” of DNA, enzyme and metallopolymer. DNA–enzyme films can also be used to produce nucleobase adduct toxicity biomarkers for detection by LC-MS. These approaches provide valuable high throughput tools for drug and chemical product development and toxicity prediction.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...