Supported ionic liquid phase rhodium nanoparticle hydrogenation catalysts
Abstract
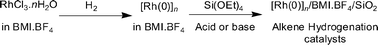
Rh(0) nanoparticles (ca. 4 nm) dispersed in an ionic liquid (1-n-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate) were immobilized within a silica network, prepared by the sol–gel method. The effect of the sol–gel catalyst (acid or base) on the encapsulated ionic liquid and Rh(0) content, on the silica morphology and texture, and on the catalyst alkene hydrogenation activity was investigated. The Rh(0) content in the resulting xerogels (ca. 0.1 wt% Rh/SiO2) was shown to be independent of the sol–gel process. However, acidic conditions afforded higher contents of encapsulated ionic liquid and xerogels with larger pore diameters, which in turn might be responsible for the higher catalyst activity in hydrogenation of the alkenes.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging strategies in catalysis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...