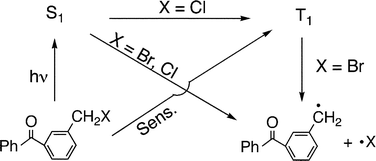
Photochemical profiles of ω-cleavage of carbon–X (X = Br and Cl) bonds in m-bromo- and m-chloromethylbenzophenones (m-BMBP and m-CMBP) were investigated by laser photolysis techniques and DFT calculations. m-BMBP and m-CMBP were found to undergo ω-bond cleavage to yield the m-benzoylbenzyl radical (m-BBR) at 295 K, and the quantum yields were determined. No CIDEP signal was detected upon 308 nm laser photolysis of both the compounds. From these observations, it was inferred that the ω-bond of these m-halomethylbenzophenones (m-HMBP) cleaves in the lowest excited singlet state (S1(n,π*)) upon direct excitation. Upon triplet sensitization of acetone (Ac), the m-BBR formation was observed in transient absorption for an Ac–m-BMBP system, and an efficiency of the C–Br bond cleavage in the lowest triplet state (T1(n,π*)) of m-BMBP was determined. In contrast, formation of triplet m-CMBP was seen for an Ac–m-CMBP system. Absence of C–Cl bond cleavage in the triplet state of m-CMBP indicated the reactive state of m-CMBP for ω-cleavage is only the S1(n,π*) state. Based on the efficiencies and DFT calculations for excited state energies, photoinduced ω-bond dissociation of m- and p-HMBPs was characterized.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...