Microparticle sampling by electrowetting-actuated droplet sweeping
Abstract
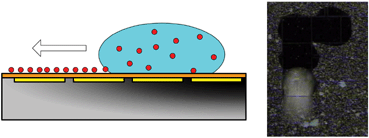
This paper describes a new microparticle sampler where particles can be efficiently swept from a solid surface and sampled into a liquid medium using moving droplets actuated by the electrowetting principle. We successfully demonstrate that super hydrophilic (2 µm and 7.9 µm diameter glass beads of about 14° contact angle), intermediate hydrophilic (7.5 µm diameter polystyrene beads of about 70° contact angle), and super hydrophobic (7.9 µm diameter Teflon-coated glass beads and 3 µm size PTFE particles of over 110° contact angles) particles on a solid surface are picked up by electrowetting-actuated moving droplets. For the glass beads as well as the polystyrene beads, the sampling efficiencies are over 93%, in particular over 98% for the 7.9 µm glass beads. For the PTFE particles, however, the sampling efficiency is measured at around 70%, relatively lower than that of the glass and polystyrene beads. This is due mainly to the non-uniformity in particle size and the particle hydrophobicity. In this case, the collected particles staying (adsorbing) on the air-to-water interface hinder the droplet from advancing. This particle sampler requires an extremely small amount of liquid volume (about 500 nanoliters) and will thus be highly compatible and easily integrated with lab-on-a-chip systems for follow-up biological/chemical analyses.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...