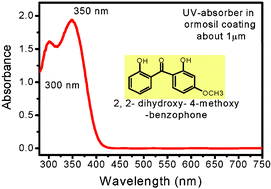
UV-protective coatings have been prepared by the sol–gel method, to reduce the destructive effects of UV radiation on easily photodegradable devices, i.e. those containing organic compounds, such as dyes and pigments or plastic materials to be used in outdoor applications. A benzophenone derivative (2,2-dihydroxy, 4-methoxybenzophenone), showing high photostability and strong absorption in the UV range, was embedded in an ormosil matrix. The usage of an organically modified silica matrix enhances the solubility of the UV absorber in the matrix allowing the preparation of highly loaded coatings. The protective coatings, prepared at room temperature, require no thermal treatment after deposition, allowing therefore their application on temperature sensitive materials. The resulting films have a strong absorption in the UV range with a thickness of only 1.0 µm. In addition, the UV-absorbing coatings are transparent, colourless, and exhibit high optical quality. The UV-protective coatings offer an easy method to prevent the photodegradation of organic materials without altering their optical properties in the visible region.
Fluorescent rhodamine dye-doped thin ormosil films were coated with a UV-protective layer in order to study their effectiveness in the reduction of the photodegradation of the dye upon irradiation with UV light. The degradation of 20% of the molecules in coated samples was 14 times slower than that of the uncoated samples. The effective temperature range of the UV-protective coatings was established by measuring the photodegradation of the samples at different temperatures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...