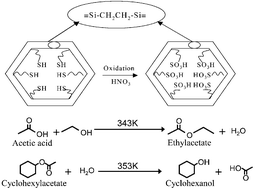
The synthesis of a new class of sulfuric acid-functionalized ethane-bridged, mesoporous hybrid organosilicas is reported where the propylsulfonic groups attached with ethane-bridged silica exhibited reasonable catalytic activity in esterification of acetic acid with ethanol as well as the hydrolysis of cyclohexylacetate. Materials were synthesized by co-condensation of ethane-bridged organosilane (MeO)3SiCH2CH2Si(OMe)3 with 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MeO)3SiCH2CH2CH2SH in the presence of octadecyltrimethylammonium chloride surfactant. Powder X-ray diffraction patterns and nitrogen sorption analysis reveal the formation of mesoporous material with uniform porosity. The maximum content of incorporated mercaptopropylsilane in the mesoporous framework obtained was 3.45 mmol g−1. The thiol (–SH) moieties of mercaptopropyl groups that protrude into the pore channels are readily accessible for further oxidation. The surface moieties functionalized with propylsulfonic groups (–CH2CH2CH2–SO3H) were generated by the controlled oxidation of propylthiol surface groups using concentrated HNO3. A maximum acid exchange capacity (acid–base titration methods) of 1.38 H+ mmol g−1 was achieved after oxidation. Further, the materials were characterized using elemental analysis, FT-IR, 29Si and 13C MAS-NMR, transmission electron microscopy and TGA. Two probe reactions, the esterification of acetic acid with ethanol and its reverse the hydrolysis of cycloacetonate, showed the significance of the material in catalytic applications. The catalytic results showed the esterification activity is comparable to that of commercial Nafion-H and also the involvement of hydrophobic nature of the material in the hydrolysis reaction.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...