Protonation effect on the excited state behaviour of EE-1-(n-pyridyl)-4-phenylbutadienes (n = 2, 3 and 4)†
Abstract
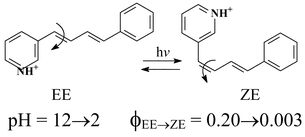
The acid–base equilibria of three aza-derivatives of EE-1,4-diphenylbutadiene and the excited state properties of their neutral and protonated forms have been studied in aqueous solutions. The prevalent relaxation of the neutral molecules is photoisomerization by a diabatic singlet mechanism accompanied by substantial internal conversion while the quantum yield of the radiative pathway is very small, particularly for the ortho- and para-substituted
- This article is part of the themed collection: In honour of Jean Kossanyi

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...