Enzymatic transformations.† Immobilized A. nigerepoxide hydrolase as a novel biocatalytic tool for repeated-batch hydrolytic kinetic resolution of epoxides
Abstract
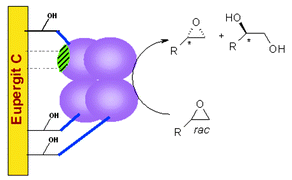
Studies aimed at immobilization of the Aspergillus niger
* Corresponding authors
a
Groupe Biocatalyse et Chimie Fine, UMR CNRS 6111, Université de la Méditerranée, Faculté des Sciences de Luminy, Case 901, 163 avenue de Luminy, 13288 Marseille Cedex 9, France
E-mail:
furstoss@luminy.univ-mrs.fr
Fax: +33 491 82 91 45
Tel: +33 491 82 91 55
b Departamento de Biocatalisis, Instituto de Catalisis, CSIC, Campus Universidad Autonoma, Cantoblanco, 28049, Madrid, Spain
Studies aimed at immobilization of the Aspergillus niger

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
C. Mateo, A. Archelas, R. Fernandez-Lafuente, J. Manuel Guisan and R. Furstoss, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2003, 1, 2739 DOI: 10.1039/B303307D
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
