Stereoelectronic substituent effects on intramolecular H-bonding in crowded o-anisic acids†
Abstract
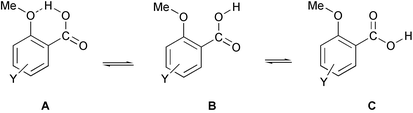
The minimum energy geometries, OH stretching frequencies, and fractional distributions of the free and intramolecularly hydrogen-bonded conformers of eleven substituted o-anisic acids were determined by density functional theory. The structural changes that are associated with formation of the intramolecular H-bond are discussed. Intensities and areas of pertinent peaks in the measured infrared spectra were used to obtain the mol fractions of the intramolecularly H-bonded conformer, in equilibrium with the intermolecularly H-bonded dimers in chloroform solution. These mol fractions follow the same order as the theoretically determined “gas phase” values. They also correlate linearly with the change in the time-averaged 13C NMR shift of the carboxyl group that is produced by a change of

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...