Adsorption and separation of cations on silica gel chemically modified by homogeneous and heterogeneous routes with the ethylenimine anchored on thiol modified silica gel
Abstract
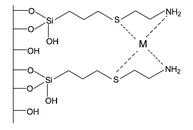
Ethyleneimine (etn) has been covalently bonded onto silica gel via homogeneous (SiSN1) and heterogeneous (SiSN2) routes. Both synthesised silica gel surfaces have been applied to adsorb divalent cations from aqueous solution at room temperature. The series of isotherms of adsorption were adjusted to a modified Langmuir equation, after collecting the data from the solid/MCl2 solution (M = Co, Ni, Cu, Pb and Hg) interfaces. The maximum adsorption were 1.08, 1.20, 1.70, 1.34 and 4.02 mmol g−1 for SiSN1 and 0.72, 1.74, 1.91, 2.19 and 2.89 mmol g−1 for SiSN2, for a the sequence of divalent cations: Co, Ni, Cu, Pb and Hg, respectively. Columns loaded with immobilised silica show resolutions (R) for separating metal ion couples: RCo–Ni = 0.22, RCo–Pb = 0.76, RCo–Cu = 1.12, : RCo–Hg = 2.06, RNi–Pb = 0.50, RNi–Cu = 1.17, RNi–Hg = 2.38, RPb–Cu = 0.33, RPb–Hg = 1.83 and RCu–Hg = 1.60 for the SiSN1 surface. The sequence: RCo–Ni = 1.10, RCo–Pb = 1.44, RCo–Cu = 1.63, : RCo–Hg = 2.26, RNi–Pb = 0.08, RNi–Cu = 0.33, RNi–Hg = 1.40, RPb–Cu = 0.38, RPb–Hg = 1.82 and RCu–Hg = 1.55 was determined for SiSN2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...