Graphene oxide/polypyrrole composites for highly selective enrichment of U(vi) from aqueous solutions
Abstract
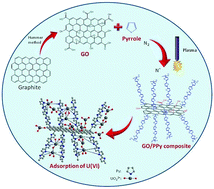
Graphene oxide/polypyrrole (GO/PPy) composites were synthesized via a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma technique in nitrogen conditions, and characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman spectroscopy, thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The sorption of U(VI) ions on GO/PPy composites from aqueous solutions was investigated as a function of contact time, pH, ionic strength and U(VI) initial concentrations. The sorption capacity of U(VI) on GO/PPy composites was much higher than those of U(VI) on GO, PPy and many other materials of today. The sorption of U(VI) on GO/PPy composites obeyed the Langmuir model, and was mainly attributed to surface complexation via the coordination of U(VI) ions with oxygen- and nitrogen-containing functional groups. The selectivity sorption of U(VI) ions on GO/PPy composites in the presence of other metal ions (i.e., Co(II), Ni(II), Cd(II), Sr(II), Zn(II)) indicated an overall preference for U(VI) ions. Moreover, the GO/PPy composites could be regenerated through the desorption of adsorbed U(VI) ions by using 1.0 M HCl solution, and cycling reused without an obvious decrease of sorption capacity. All these performances indicate that GO/PPy composites are suitable materials for the highly selective removal and preconcentration of U(VI) ions from aqueous solutions in environmental pollution management.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...