Long and short term impacts of CuO, Ag and CeO2 nanoparticles on anaerobic digestion of municipal waste activated sludge
Abstract
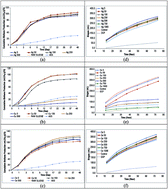
In this study, long and short term inhibition impacts of Ag, CuO and CeO2 nanoparticles (NPs) on anaerobic digestion (AD) of waste activated sludge (WAS) were investigated. CuO NPs were detected as the most toxic NPs on AD. As the CuO NP concentration increased from 5 to 1000 mg per gTS, an increase in the inhibition of AD from 5.8 to 84.0% was observed. EC50 values of short and long term inhibitions were calculated as 224.2 mgCuO per gTS and 215.1 mgCuO per gTS, respectively. Ag and CeO2 NPs did not cause drastic impacts on AD as compared to CuO NPs. In the long term test, Ag NPs created 12.1% decrease and CeO2 NPs caused 9.2% increase in the methane production from WAS at the highest dosage. FISH imaging also revealed that the abundance of Archaea in raw WAS was similar in short and long term tests carried out with WAS containing Ag and CeO2 NPs. On the other hand, CuO NPs caused inhibition of Archaea in the long term test. Digestion kinetics of WAS containing Ag, CeO2, CuO NPs were also evaluated with Gompertz, Logistic, Transference and First Order models. The hydrolysis rate constant (kH) for each concentration of Ag and CeO2 NPs and the raw WAS was 0.027745 d−1 while the kH of WAS containing high concentrations of CuO NPs was found to be 0.001610 d−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...