Influence of cell size on cellular uptake of gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
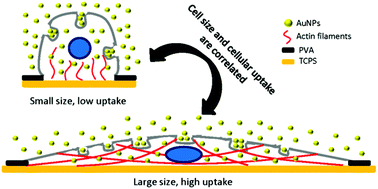
Nanoparticles (NPs) have shown great potential for biomedical applications because of their unique physical and structural properties. A critical aspect for their clinical applications is cellular uptake that depends on both particle properties and the cell mechanical state. Despite the numerous studies trying to disclose the influencing factors, the role of cell size on cellular uptake remains unclear. In this study, poly(vinyl alcohol) was micropatterned on tissue culture polystyrene surfaces using UV photolithography to control the cell size, and the influence of cell size on the cellular uptake of gold NPs was investigated. Cells with a large size had a high total cellular uptake, but showed a low average uptake per unit area of cells. Cells with a small size showed opposite behaviors. The results were related to both cell/NP contacting area and membrane tension. A large cell size was beneficial for a high total cellular uptake due to the large contact area with the NPs. On the other hand, the large cell size resulted in high membrane tension that required high wrapping energy for engulfing of NPs and thus reduced the uptake. The two oppositely working effects decided the cellular uptake of NPs. The results would shed light on the influence of the cellular microenvironment on cellular uptake behavior.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...