Theoretical insight of reactive oxygen species scavenging mechanism in lignin waste depolymerization products†
Abstract
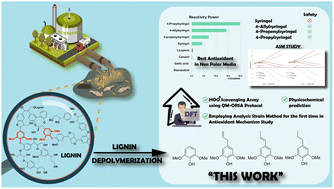
Apart from natural products and synthesis, phenolic compounds can be produced from the depolymerization of lignin, a major waste in biofuel and paper production. This process yields a plethora of aryl propanoid phenolic derivatives with broad biological activities, especially antioxidant properties. Due to its versatility, our study focuses on investigating the antioxidant mechanisms of several phenolic compounds obtained from renewable and abundant resources, namely, syringol (Hs), 4-allylsyringol (HAs), 4-propenylsyringol (HPns), and 4-propylsyringol (HPs). Employing the density functional theory (DFT) approach in conjunction with the QM-ORSA protocol, we aim to explore the reactivity of these compounds in neutralizing hydroperoxyl radicals in physiological and non-polar media. Kinetic and thermodynamic parameter calculations on the antioxidant activity of these compounds were also included in this study. Additionally, our research utilizes the activation strain model (ASM) for the first time to explain the reactivity of the HT and RAF mechanisms in the peroxyl radical scavenging process. It is predicted that HPs has the best rate constant in both media (1.13 × 108 M−1 s−1 and 1.75 × 108 M−1 s−1, respectively). Through ASM analysis, it is observed that the increase in the interaction energy due to the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds during the reaction is an important feature for accelerating the hydrogen transfer process. Furthermore, by examining the physicochemical and toxicity parameters, only Hs is not suitable for further investigation as a therapeutic agent because of potential toxicity and mutagenicity. However, overall, all compounds are considered potent HOO˙ scavengers in lipid-rich environments compared to previously studied antioxidants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...