DRGD-linked charged EKKE dimeric dodecapeptide: pH-based amyloid nanostructures and their application in lead and uranium binding†
Abstract
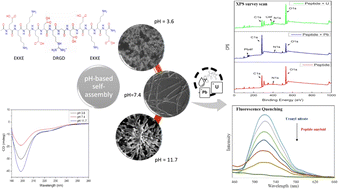
Peptides have been reported to undergo self-assembly into diverse nanostructures, influenced by several parameters, including their amino acid sequence, pH, charge, solvent, and temperature. Inspired by natural systems, researchers have developed biomimetic peptides capable of self-assembling into supramolecular functional structures. The present study explored a newly designed peptide sequence, EKKEDRGDEKKE, where E = glutamic acid, K = lysine, D = aspartic acid, G = glycine, and R = arginine, with a metal binding DRGD sequence incorporated between the exclusively charged EKKE peptide. We investigated the formation and the potential of the EKKEDRGDEKKE peptide in retaining the structure and morphology adopted by the individual EKKE peptide. According to a combination of experimental techniques such as thioflavin T fluorescence, field emission-scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and circular dichroism, it was evident that the EKKEDRGDEKKE peptide displayed a pH-dependent propensity to adopt amyloid-like structures. Furthermore, the self-assembled entities formed under acidic, basic, and neutral conditions exhibited morphological variations, which resembled that observed for the exclusively charged EKKE peptide. Furthermore, the incorporation of the functional DRGD motif resulted in promising binding to two toxic metal ions, lead (Pb) and uranium (U), as evidenced by a range of spectroscopic techniques, including UV-visible spectroscopy, atomic absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The use of the amyloid-forming EKKEDRGDEKKE scaffold can also be extended to potential biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...