Effect of mass ratio on micro-mesoporous Cu-SSZ-13/CeWTi composite catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia
Abstract
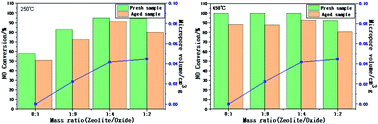
A series of micro-mesoporous SSZ-13/CexWyTiz composites with different zeolite/oxide ratios were synthesized using a one-step crystallization method. The effects of the mass ratio on the crystal form, specific surface area, pore structure, surface element properties, redox properties, surface acidity and deNOx performance of the Cu-SSZ-13/CeWTi composite catalysts were investigated using X-ray diffractometry (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller analysis (BET), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), H2 temperature programmed reduction (H2-TPR) and NH3 temperature programmed desorption (NH3-TPD). The results reveal that the Cu-SSZ-13/CeWTi composite catalysts formed a micro-mesoporous structure. The increase in the mass ratio leads to the increased microporous ratio of the composite catalysts, the improved crystal structure of SSZ-13 and a higher specific surface area and pore volume, which is conducive to enhancing the low-temperature deNOx activity, but its high-temperature performance (450 °C and above) decreases. The introduction of micropores into mesoporous materials can result in the production of more Ce4+, surface chemisorption oxygen species Oα and acid sites. The Cu-SSZ-13/CeWTi composite catalyst with a mass ratio of 1 : 4 demonstrated the best micro-mesoporous ratio, low-temperature selective catalytic reduction (SCR) performance and hydrothermal stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...