A novel MnO–CrN nanocomposite based non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor†
Abstract
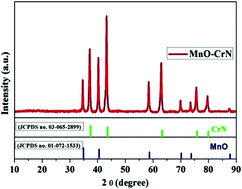
A MnO–CrN composite was obtained via the ammonolysis of the low-cost nitride precursors Cr(NO3)3·9H2O and Mn(NO3)2·4H2O at 800 °C for 8 h using a sol–gel method. The specific surface area of the synthesized powder was measured via BET analysis and it was found to be 262 m2 g−1. Regarding its application, the electrochemical sensing performance toward hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was studied via applying cyclic voltammetry (CV) and amperometry (i–t) analysis. The linear response range was 0.33–15 000 μM with a correlation coefficient (R2) value of 0.995. Excellent performance toward H2O2 was observed with a limit of detection of 0.059 μM, a limit of quantification of 0.199 μM, and sensitivity of 2156.25 μA mM−1 cm−2. A short response time of within 2 s was achieved. Hence, we develop and offer an efficient approach for synthesizing a new cost-efficient material for H2O2 sensing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...