A novel colorimetric immunoassay for sensitive monitoring of ochratoxin A based on an enzyme-controlled citrate-iron(iii) chelating system†
Abstract
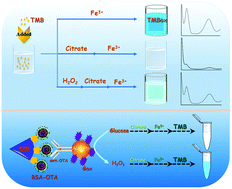
Biotoxins present in foods represent a major source of contamination. Although different analytical methods have been developed, a new detection method for identification and quantification of these toxins is necessary for extending their application sphere. Therefore, in this study, an enzyme-controlled citrate-iron(III) chelating system was used to build a novel colorimetric immunoassay sensing platform for detection of ochratoxin A (OTA). The experimental signal was derived from the reaction of iron(III) and 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB). However, the addition of citrate could combine with iron(III) rapidly, thereby hindering the reaction of iron(III) and TMB for production of the signal (i.e., colorless to blue). Additionally, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which could be produced from glucose in the presence of glucose oxidase (GOx), could affect the binding capacity of citrate and iron(III), thereby releasing iron(III) to react with TMB. That is to say, different amounts of GOx could regulate the intensity of the signal. Based on these findings, magnetic bead (MB)-based OTA competed with dissociative OTA (added) for glucose oxidase (GOx)-labelled anti-OTA. As the dissociative OTA concentration increased, the amount of GOx-labelled anti-OTA on MB conveniently reduced and the absorbance decreased. The method exhibited a good linear relationship as the concentration of the target (OTA) increased from 0.005 to 5 ng mL−1; the detection limit was 4.2 pg mL−1, as estimated based on the 3Sblank level under optimal conditions. The specificity and feasibility for a real sample of the colorimetric immunoassay was acceptable, respectively. The current results provided important insights into the development of citrate-iron(III) chelating system-based biological detection methods and colorimetric immunoassays.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...