Self-repairing microcapsules with aqueous solutions as core materials for conductive applications†
Abstract
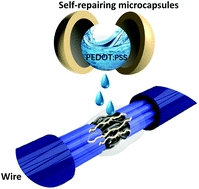
The utilization of expensive metal liquids or volatile organic solvents as core parts in conductive microcapsules causes the depletion of metal resources and the formation of smog, limiting the sustainable development of self-repairing electronics. In this work, we report the first novel family of self-healing microcapsules with aqueous conductive core materials, in which inexpensive, non-toxic, and non-polluting aqueous solutions are employed as the continuous phase and the dispersed phase. These microcapsules with a shell of melamine–formaldehyde resin and a core of aqueous solutions were successfully fabricated through an in situ polymerization method. The prepared microcapsules showed uniform core–shell spherical structures with a size range of 10–20 μm. With excellent thermodynamic properties, these microcapsules had a phase change latent heat, which would be helpful to reduce the temperature of the circuit itself during the long-term operation of the device. Moreover, these self-repairing microcapsules can withstand pressures up to ∼14 N and demonstrated great pressure resistance. In particular, the best electrical conductivity of these microcapsules with aqueous core materials reached 6.232 ms cm−1. Finally, the self-repairing application of these microcapsules was verified by a regulated bulb lighting system. We anticipate that these self-healing microcapsules with aqueous conductive core materials would have great potential applications for the sustainable development of electronics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...