Derivatization-assisted enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for identifying hallucinogenic mushrooms with enhanced sensitivity
Abstract
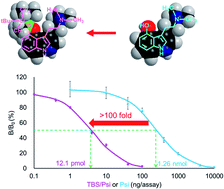
A sensitive immunochemical method for identifying hallucinogenic mushrooms (magic mushrooms) is required for regulating their illicit use. We have previously generated a monoclonal antibody (mAb) that targets psilocin (Psi), the major psychoactive compound in hallucinogenic mushrooms, and developed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). However, this ELISA failed to achieve the expected low-picomole-range sensitivity, as a result of insufficient affinity of the mAb to Psi. It is recognized that haptenic antigens with a larger molecular mass tend to induce antibodies with higher affinities. Thus, we herein report a “derivatization-assisted ELISA,” in which the “real analyte” Psi was determined as a “surrogate analyte,” the tert-butyldimethylsilyl ether analog thereof (TBS/Psi) having a 1.6-fold greater molecular mass (Mr 318.53) than Psi. A novel mAb against TBS/Psi, prepared by immunizing mice with a TBS/Psi–albumin conjugate showed a 69-fold higher affinity to TBS/Psi residues (Ka = 3.6 × 107 M−1 as IgG) than that of our previous mAb against Psi. This mAb consequently enabled a competitive ELISA for measuring TBS/Psi with the desired sensitivity: the dose–response curve midpoint (12.1 pmol per assay) was >100-fold lower than that of the previous ELISA for determining Psi. Extracts of dried mushroom powders were mixed with TBS triflate for 30 min at room temperature, converting Psi into TBS/Psi in approximately 50% yield. The reaction mixture was then subjected to an ELISA using the anti-TBS/Psi mAb to determine TBS/Psi. Psilocybe cubensis, a species of hallucinogenic mushrooms, gave rise to positive signals, indicating the presence of Psi therein in the expected quantity, while no detectable response was observed for four kinds of edible mushrooms available in the markets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...