An in vivo bioelectronic nose for possible quantitative evaluation of odor masking using M/T cell spatial response patterns†
Abstract
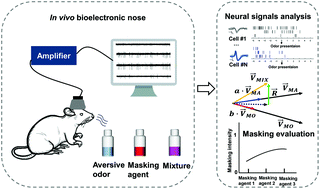
Odor masking is a prominent phenomenon in the biological olfactory perception system. It has been applied in industry and daily life to develop masking agents to reduce or even eliminate the adverse effects of unpleasant odors. However, it is challenging to assess the odor masking efficiency with traditional gas sensors. Here, we took advantage of the olfactory perception system of an animal to develop a system for the evaluation and quantification of odor masking based on an in vivo bioelectronic nose. The linear decomposition method was used to extract the features of the spatial response pattern of the mitral/tufted (M/T) cell population of the olfactory bulb of a rat to monomolecular odorants and their binary mixtures. Finally, the masking intensity was calculated to quantitatively measure the degree of interference of one odor to another in the biological olfactory system. Compared with the human sensory evaluation reported in a previous study, the trend of masking intensity obtained with this system positively correlated with the human olfactory system. The system could quantitatively analyze the masking efficiency of masking agents, as well as assist in the development of new masking agents or flavored food in odor or food companies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...