Effects of ozone treatment on SOD activity and genes in postharvest cantaloupe
Abstract
Ozone has been shown to play a positive role in the storage and preservation of agricultural products. However, there is little research on the cantaloupe preservation mechanism of ozone treatment (OT), especially the effect on superoxide dismutase (SOD) and the mechanism of scavenging superoxide anion 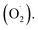 In this study, xizhoumi 25 was used as a typical cantaloupe material to detect
In this study, xizhoumi 25 was used as a typical cantaloupe material to detect 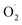 content, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and SOD enzyme activity in the pericarp and pulp, respectively, and transcriptomics and qRT-RCR were used for cantaloupe SOD family gene expression. The results showed that the rate of
content, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and SOD enzyme activity in the pericarp and pulp, respectively, and transcriptomics and qRT-RCR were used for cantaloupe SOD family gene expression. The results showed that the rate of 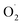 and H2O2 content were inhibited and SOD activity was higher in the treatment group compared with the control (CK) group in the pericarp and pulp; SOD was more active in the pericarp and was higher than that in the pulp. The transcription level of Cu/Zn-SOD, identified as the most abundant component of the cantaloupe SOD gene family, was promoted in the OT group, especially the key gene Cu/Zn-SOD-1. The expression level of the Fe-SOD gene was promoted in the pericarp but regulated in the pulp, while the expression of the Mn-SOD gene was down-regulated in the OT group in both pericarp and pulp. In addition, the results of qRT-PCR were consistent with the transcriptome results. Correlation analysis showed that OT not only enhanced the positive correlation between
and H2O2 content were inhibited and SOD activity was higher in the treatment group compared with the control (CK) group in the pericarp and pulp; SOD was more active in the pericarp and was higher than that in the pulp. The transcription level of Cu/Zn-SOD, identified as the most abundant component of the cantaloupe SOD gene family, was promoted in the OT group, especially the key gene Cu/Zn-SOD-1. The expression level of the Fe-SOD gene was promoted in the pericarp but regulated in the pulp, while the expression of the Mn-SOD gene was down-regulated in the OT group in both pericarp and pulp. In addition, the results of qRT-PCR were consistent with the transcriptome results. Correlation analysis showed that OT not only enhanced the positive correlation between 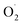 and H2O2 in the whole cantaloupe and the negative correlation between
and H2O2 in the whole cantaloupe and the negative correlation between 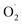 and SOD activity in the pericarp but also altered the correlation between SOD genes and
and SOD activity in the pericarp but also altered the correlation between SOD genes and 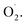 The mechanism of
The mechanism of 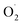 regulation in postharvest cantaloupe treated with ozone may be through stimulating the SOD activity and altering the expression of related genes in the pericarp and pulp.
regulation in postharvest cantaloupe treated with ozone may be through stimulating the SOD activity and altering the expression of related genes in the pericarp and pulp.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...