Ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of dopamine by a NiFeP based flexible electrochemical sensor†‡
Abstract
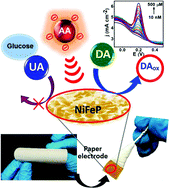
A ultrasensitive NiFeP based electrochemical sensor was developed for the selective electrochemical detection of dopamine to address the issue associated with neurological disorders including Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. The novel sensor shows superior selectivity and sensitivity with a lowest detection limit of 0.3 nM and a wide detection range of 10 nM–500 μM and is immune to the interference of ascorbic acid at physiological pH (7.4). A novel flexible sensor was developed with NiFeP coated over Whatman filter paper, which exhibits two liner ranges of 10 nM−1 μM and 10 μM–500 μM with an ultra high sensitivity of 756 μA μM−1 cm−2 and 4.6 μA μM−1 cm−2 respectively with a wide detection range of 10 nM to 500 μM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...