Enhanced UV-Vis-NIR activated photocatalytic activity from Fe3+-doped BiOBr:Yb3+/Er3+ upconversion nanoplates: synergistic effect and mechanism insight†
Abstract
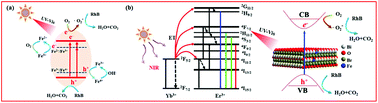
Upconversion (UC) materials are recognized as promising candidates to harvest solar energy for photocatalysis. In this work, a simple strategy for simultaneously enhancing the UC luminescence and photocatalytic efficiency of BiOBr:Yb3+/Er3+ nanoplates through Fe3+ ion doping is reported. Compared to the Fe3+-free sample, the UC emission intensity was significantly enhanced through tailoring of the crystal symmetry by Fe3+ ions. Experiment and DFT calculations reveal that the introduction of Fe3+ ions resulted in the formation of an impurity energy level, extending to the light absorption region. As expected, the Fe3+-doped BiOBr:Yb3+/Er3+ nanoplates exhibit a wide photoresponse from the UV to NIR regions, good stability, and obviously enhanced photocatalytic activities compared with the BiOBr:Yb3+/Er3+ nanoplates in the degradation of RhB. The boosted photocatalytic activity can be attributed to the synergic effect of the efficient utilization of UC luminescence and Fe3+ doping, where Fe3+ doping could improve the light harvesting capacity, enhance the separation efficiency of electron and hole (e−/h+) pairs, and promote the production of highly oxidative species. This work not only provides a promising system for the efficient utilization of solar light, but also offers a feasible guideline for the further design of broad-spectrum active photocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...