Anoxic photocatalytic treatment of synthetic mining wastewater using TiO2 and scavengers for complexed cyanide recovery†
Abstract
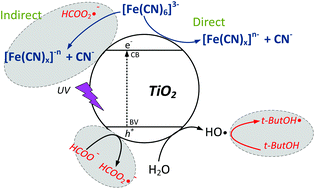
The wastewater from gold exploitation is well known for the toxic nature of recalcitrant cyanide metallic complexes. In this work the selectivity in the photocatalytic degradation of gold mining wastewater (Fe(CN)63−) using suspended TiO2 with alcoholic and organic acid scavengers in a mini-CPC photoreactor with a 30 W UV-A LED as an artificial source of light was evaluated. The study was done in four stages: 1. load catalyst determination, 2. combination of scavengers in a typical photocatalytic degradation, 3. evaluation of scavenger concentration and 4. kinetic study. The decomposition into CN− and Fe removal of the cyanocomplex were tracked. It was observed that formic acid (FA) and t-butanol (t-ButOH) were the best scavengers for the photocatalytic degradation under anoxic conditions. The best concentrations of acceptors used in the study were 10 mM FA and 10 mM t-ButOH at 20 W m−2 of UV-A power, reaching 80% degradation of Fe(CN)63−, 40% Fe removal and 18 ppm of free cyanide CN release to the liquid phase. The electrical efficiency of oxidation per order (EEo) was increased by about 50% with the addition of scavengers instead of traditional anoxic photocatalytic treatment. It was proved that the photocatalytic decomposition of the Fe cyanocomplex was done through the photoreduction path of the metal complex.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Solar chemistry & photocatalysis: environmental applications – SPEA10


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...