Label-free and highly sensitive fluorescence detection of lead(ii) based on DNAzyme and exonuclease III-assisted cascade signal amplification†
Abstract
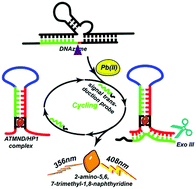
Routine detection of trace amounts of Pb2+ is of significant importance because it poses severe risks to human health and the environment. In this paper, a novel label-free fluorescence platform for the sensitive detection of Pb2+ has been successfully constructed by using Pb2+-specific 8–17 DNAzyme as the molecular recognition element, 2-amino-5,6,7-trimethyl-1,8-naphthyridine (ATMND) as the signal reporter, and exonuclease III (Exo III) as the signal amplifier. A good linearity between the fluorescence intensity and the logarithm of Pb2+ concentration was obtained in the range from 100 pM to 10 μM with a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.99. The sensing system exhibited ultrasensitivity towards Pb2+ at low concentration (50 pM) without any labeling, modification, immobilization, or washing procedure. Besides, the proposed method was also highly selective for Pb2+ against other metal ions. This biosensor was robust and can be applied for the determination of Pb2+ in complex samples with desired recovery and good accuracy. With the successful demonstration of Pb2+ detection, the label-free biosensor can be readily expanded to monitor other targets in a simple, cost-effective, and ultrasensitive way by replacing the target-specific molecular recognition elements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...