EMA-amplicon-based taxonomic characterisation of the viable bacterial community present in untreated and SODIS treated roof-harvested rainwater†
Abstract
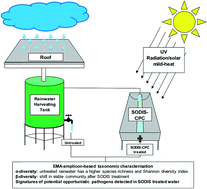
Illumina next generation sequencing coupled with the viability dye ethidium monoazide bromide (EMA) was utilised to characterise and compare the viable bacterial community present in roof-harvested rainwater pre- and post-treatment. The diversity and relative abundance of the viable bacterial community present in roof-harvested rainwater before (tank 1) and after solar disinfection treatment (SODIS-CPC-1) for eight h, was also determined. Taxonomic assignments were made using the Ribosomal Database Project whereafter alpha- and beta-diversity indices were calculated to investigate the effect of SODIS treatment on the viable bacterial population present in roof-harvested rainwater. Alpha-diversity indices, including species richness and Shannon diversity were significantly (p < 0.05) lower in the SODIS-CPC-1 treated rainwater samples in comparison to tank 1 rainwater samples, indicating a significant difference in the species richness after treatment. The tank 1 rainwater samples were dominated by the families Nocardiaceae (16.5%) and Pseudomonadaceae (8.9%), while the SODIS-CPC-1 rainwater samples were dominated by Nocardiaceae (44.0%) and Micrococcaceae (31.7%). On the genus level, Rhodococcus (17.1%) and Pseudomonas (9.2%) dominated in the tank 1 rainwater samples, while Rhodococcus (48.0%) and Arthrobacter (35.2%) were the most abundant in the SODIS-CPC-1 rainwater samples. While, viable opportunistic pathogenic bacteria such as Pseudomonas and Clostridium XI were detected in both the tank 1 and SODIS-CPC-1 rainwater samples, beta-diversity analysis, using the Bray-Curtis distance metric system, indicated that there was a significant shift (PERMANOVA, p < 0.05) in the viable bacterial community after SODIS treatment. Based on the results obtained, EMA-amplicon-based taxonomic analysis could be utilised as an alternative culture-independent method for the initial monitoring and profiling of the viable and viable-but-non-culturable whole bacterial community in water sources.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...