Understanding segregation processes in SAMs formed by mixtures of hydroxylated and non-hydroxylated fatty acids†
Abstract
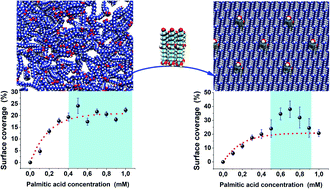
In this paper, we focus on the segregation processes emerging when preparing mixtures with different compositions of aleuritic (9,10,16 trihydroxyhexadecanoic) (ALE) and palmitic (hexadecanoic) (PAL) acids. The combination of atomic force microscopy (AFM) and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations enabled us to prove the role of the functional groups in the formation of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on muscovite mica surfaces. MD simulations indicate that segregation processes are favored in high ALE composition mixtures in agreement with the experimental evidence, whereas low ALE compositions promote the co-existence between segregated and dispersed systems. The secondary hydroxyl groups play a central role in the self-assembling mechanism because they control the formation of hydrogen bonding networks guarantying system stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...