Nanostructure and device architecture engineering for high-performance quantum-dot light-emitting diodes
Abstract
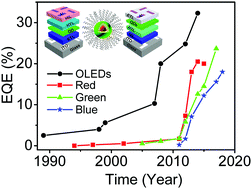
Quantum-dot-based light-emitting diodes (QD-LEDs) have attracted considerable attention owing to their high color purity, size-dependent emission wavelength tunability, and solution processing ability as well as their inherent photo- and thermal-stability, making them suitable candidates for next-generation flat-panel displays and solid-state lighting. In the last few decades, tremendous progress has been achieved in increasing the lifetime and efficiency of QD-LEDs, with the maximum external quantum efficiency (ηEQE) of the red- and green-emitting QD-LEDs reaching 20.5% and 23.68%, respectively. These efficiencies are comparable to state-of-the-art phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and the operational lifetimes of red- and green-emitting QD-LEDs have satisfied the requirements for use in commercial displays. In comparison with the red- and green-emitting QD-LEDs, blue-emitting QD-LEDs exhibit a lower lifetime and device efficiency. Even though the maximum ηEQE can reach 18%, the lifetime is only about 1000 h, which falls short of the basic requirements for commercial displays (>10 000 h). In this review, we present the improvements made in the device performance of QD-LEDs through optimization of the quantum dot (QD) emitting layer and device architectures. The optimization of the QD emitting layer, the effects of the nanostructure-tailoring and surface-engineering of the quantum dots on the device performance are highlighted. Moreover, owing to the toxicity of Cd-based QD-LEDs, advances in the performance of heavy-metal-free QD-LEDs are also emphasized. Furthermore, the optimization of device architectures, the progress of the device performance and the working mechanism are outlined, based on the four types of QD-LEDs. Finally, we present the challenges and future perspectives facing researchers who are developing QD-LEDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...