Reduced Pyronin B as a solution-processable and heating-free n-type dopant for soft electronics†
Abstract
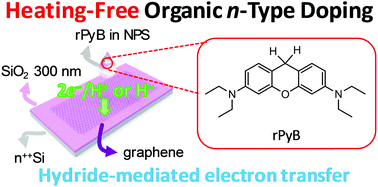
Air-stable and heating-free doping processes are highly desirable for realizing advanced flexible electronics on plastic substrates. A synthetic protocol for a high-performance n-type organic dopant using an organic cationic dye, Pyronin B, via a simple chemical reduction method with NaBH4 in various organic non-polar solvents is developed, in which the cationic dye Pyronin B is transformed into its leuco form. The reduced Pyronin B (rPyB, leuco form) spontaneously interacts with carbon nanomaterials, such as graphene and [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM), via hydride-mediated electron transfer doping, which is confirmed by electron spin resonance (ESR) analysis. After coating rPyB onto graphene, the non-polar solvents are removed by simple evacuation (∼1 × 10−3 Torr) without an annealing step. The work function of graphene is reduced from 4.52 eV to 3.98 eV after doping. Multiple coatings of rPyB on graphene field-effect transistors (FETs) result in air stability for 90 days under ambient conditions. Selective n-type doping using a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) stamp and rPyB has also been performed on a large-area 16 × 16 graphene FET array. Our findings demonstrate a viable methodology for the cost-effective synthesis of an n-type dopant and its application in soft electronics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...