Highly sensitive detection of polarized light using a new group IV–V 2D orthorhombic SiP†
Abstract
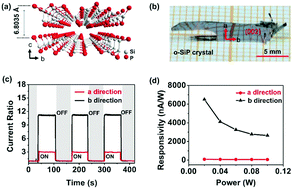
Group IV–V 2D semiconductors, such as GeP and GeAs, have attracted increasing attention as a hot research topic due to their high in-plane anisotropic properties. As one among them, orthorhombic SiP (o-SiP) deserves more attention due to its sufficiently high carrier mobility, large band gap, excellent stability and even a direct band gap in the monolayer. In this work, the experimental Raman modes were identified based on DFT calculations and then we demonstrated highly in-plane anisotropy of the phonon vibrations by angle-resolved polarized Raman spectroscopy. In addition, o-SiP based photodetectors were fabricated to investigate the in-plane anisotropic photoresponse. The results indicate that o-SiP is an alternative photodetector with high responsivity and well-reproducible cycles. Furthermore, high anisotropy was revealed with a notably anisotropic on/off switching ratio. Our results show that o-SiP is a new member of the family of group IV–V 2D semiconductors with intriguing optoelectronic properties, and will open new opportunities for promising applications in advanced photonic and optoelectronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...