Doping Y2O3 with Mn4+ for energy-efficient lighting
Abstract
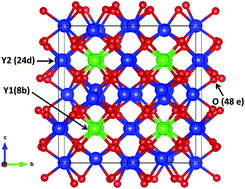
Developing energy-efficient LEDs that emit warm white light requires new red phosphors with appropriate emission wavelengths and band widths. Mn4+-activated Y2O3 is a potential red LED phosphor with narrow emission and improved emission wavelength compared to previously known Mn4+-activated oxide phosphors. In this work, the dopability and the oxidation state of Mn in Y2O3 are investigated based on the formation energies of native defects, Mn dopants, and divalent co-dopants (i.e., Ca, Sr, Cd, and Zn) calculated using hybrid density functional theory. We found that Mn4+ is difficult to form in Y2O3 without co-doping. Stabilizing Mn4+ on Y3+ sites (forming Mn+Y donors) requires the co-doping of compensating acceptors (Ca or Sr) in oxygen-rich growth environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
