A ‘turn-on’ fluorescent probe for lysosomal phosphatase: a comparative study for labeling of cancer cells†
Abstract
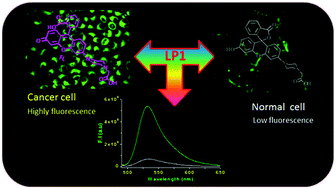
We have described the ability of a newly synthesized fluorescent probe (LP1) to detect phosphatase activity in lysosomes in cancer cells. Probe LP1 displayed a 33-fold fluorescence intensity enhancement at λem 532 nm in the presence of phosphatase in HEPES buffer (pH 4.5). The quantum yield of probe LP1 was increased by ∼21-fold upon exposure to phosphatase at acidic pH. The probe LP1 is highly chemoselective toward phosphatase (ALP/ACP) and is insensitive to interference by ubiquitous biological analytes. The high cell adhesion property and cell viability of LP1 indicate that LP1 is biocompatible and nontoxic; these two characteristic features make it a suitable candidate for phosphatase tracking in living cells. LP1 dose-dependent fluorescence images in living cells suggested that the expression of phosphatase in cancer cells (HeLa) is 2-fold higher as compared to the normal NIH-3T3 cells. The colocalization images confirmed that LP1 was exclusively localized in lysosomes. We envision that LP1 could be a potential tool in clinical diagnosis for discriminating cancer cells from normal cells depending on the expression of phosphatase in lysosomes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...