Surface zwitterionization on versatile hydrophobic interfaces via a combined copolymerization/self-assembling process†
Abstract
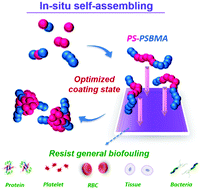
Amphiphilic zwitterionic copolymers have a severe problem of solubility, which restricts the feasibility and development of antifouling coatings. In this work, zwitterionic polymers were grafted via a novel modification method, namely, in situ self-assembling coating (ISC), which consists of synthesizing and simultaneously coating a copolymer onto a surface. This resolves the dissolution problem of amphiphilic zwitterionic copolymers. Here, the ISC method was applied to a copolymer composed of hydrophobic styrene (ST) and hydrophilic sulfobetaine methacrylate (SBMA). Under optimized conditions of concentration, molar ratio, and reaction time, the amphiphilic copolymer, poly(styrene-co-sulfobetaine methacrylate) (PS-PSBMA), can be coated onto the substrate surface. Ultralow protein adsorption from single-protein solutions and reduction of attachments from human blood platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes, tissue cells, and bacteria were achieved. The mechanism of ISC was explained by carrying out time-dependent fibrinogen adsorption tests, along with particle size measurements in the polymerization bath. Furthermore, the ISC method was applied to versatile hydrophobic materials including polypropylene (PP), poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS), and poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (PTFE). This work introduces a unique, convenient, and efficient method for synthesizing and coating amphiphilic zwitterionic polymers in a single step for antifouling applications in complex media.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry B HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...