The promoting effect on pre-osteoblast growth under electrical and magnetic double stimulation based on PEDOT/Fe3O4/PLGA magnetic-conductive bi-functional scaffolds
Abstract
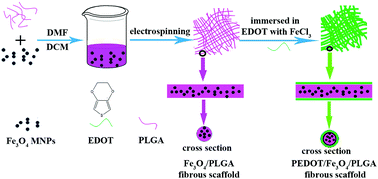
Electrical stimulation (ES) and magnetic stimulation (MS) can promote bone tissue formation in vivo. Loading ES and MS simultaneously would be very beneficial for bone tissue construction in vitro or in vivo. Magnetic-conductive bi-functional scaffolds which are favorable for the transfer of ES and MS, could further facilitate bone cell/tissue growth. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT)/Fe3O4/polylactic acid-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) magnetic-conductive bi-functional fibrous scaffolds were prepared through in situ polymerization of EDOT on Fe3O4/PLGA fibers. MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts were incubated on the PEDOT/Fe3O4/PLGA fibrous scaffolds and were stimulated by electrical, magnetic and electrical–magnetic signals respectively to detect the impact of different stimulation on cell viability. The measured results show that the scaffolds possess good conductivity and superparamagnetic responsiveness. Furthermore, both electrical and magnetic stimulation promoted cell proliferation and magnetic stimulation could induce cell alignment arrangement. Meanwhile, under electrical–magnetic double stimulation, cell viability was much higher than for cells under single electrical or magnetic stimulation. The growth promoting effects of PEDOT/Fe3O4/PLGA fibrous scaffolds under electrical–magnetic double stimulation has great practical potential for bone tissue engineering.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...