Hyperthermia properties of hyaluronic acid-coated La0.7Sr0.3−xBaxMnO3 nanoparticles
Abstract
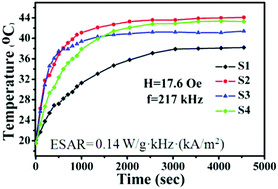
In this work, La0.7Sr0.3−xBaxMnO3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.15) magnetic nanoparticles were synthesized using a simple sol–gel method in the presence of polyvinyl alcohol as a chelating agent. Then the nanoparticles are coated by hyaluronic acid as the surfactant via high-energy ball milling for their possible application in biocompatible magnetic fluid hyperthermia. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, vibrating sample magnetometry, scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and high-frequency induction heating studies. It was found that the hyaluronic acid-coated La0.7Sr0.25Ba0.05MnO3 nanoparticles, with a particle diameter of ∼100 nm and a Curie temperature of 67 °C at a concentration of 5 mg mL−1, gave the optimal induction heating results. The saturation heating temperature, the specific absorption rate, and the effective specific absorption rate are 44.1 °C, 60.1 W g−1 and 0.14 W g−1 kHz (kA m−2), respectively. The hyaluronic acid-coated La0.7Sr0.25Ba0.05MnO3 nanoparticles with a suitable saturation heating temperature and a high specific absorption rate can be used as an effective heating source for the hyperthermia treatment of cancer. Their targeting ability towards cancer cells and good biocompatibility were also proved by cell experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...