Strategies to design antimicrobial contact lenses and contact lens cases
Abstract
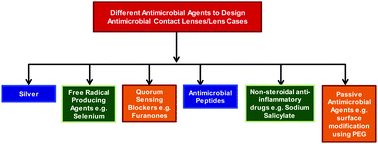
Contact lens wear is a primary risk factor for developing ocular complications, such as contact lens acute red eye (CLARE), contact lens-induced peripheral ulcer (CLPU) and microbial keratitis (MK). Infections occur due to microbial contamination of contact lenses, lens cases and lens care solution, which are exacerbated by extended lens wear and unsanitary lens care practices. The development of microbial biofilms inside lens cases is an additional complication, as the developed biofilms are resistant to conventional lens cleaning solutions. Ocular infections, particularly in the case of MK, can lead to visual impairment or even blindness, so there is a pressing need for the development of antimicrobial contact lenses and cases. Additionally, with the increasing use of bandage contact lenses and contact lenses as drug depots and with the development of smart contact lenses, contact lens hygiene becomes a therapeutically important issue. In this review, we attempt to compile and summarize various chemical strategies for developing antimicrobial contact lenses and lens cases by using silver, free-radical producing agents, antimicrobial peptides or by employing passive surface modification approaches. We also evaluated the advantages and disadvantages of each system and tried to provide input to future directions. Finally, we summarize the developing technologies of therapeutic contact lenses to shed light on the future of contact lens applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...