An adaptive and stable bio-electrolyte for rechargeable Zn-ion batteries†
Abstract
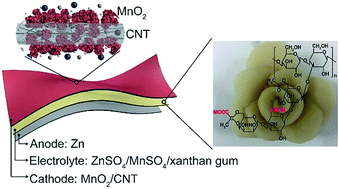
Sulfate solutions with high safety, low cost and wide electrochemical windows are widely used as electrolytes for aqueous batteries. However, the practical application of such batteries, especially for wearable devices, is still limited by the lack of a stable polymer electrolyte, due to the strong ability of the favorably selected sulfate electrolytes to precipitate polymers. Herein, we report a very stable sulfate-tolerant gum bio-electrolyte prepared by readily mixing the xanthan bio-polymer with aqueous sulfate solutions. The gum electrolyte is highly conductive (1.46 × 10−2 S cm−1), hydrating, adhesive, and adaptive. Zn-ion batteries assembled using such gum electrolytes show competitive performance in aqueous batteries, which include high capacities (about 260 mA h g−1 for MnO2 at 1C), high rate capability, good cyclability (about 90% capacity retention and about 100% coulombic efficiency over 330 cycles at 1C, and about 127 mA h g−1 capacity over 1000 cycles at 5C), and high durability to bending and twisting. Moreover, the use of the gum electrolyte could prohibit the growth of zinc dendrites. Considering the wide suitability of aqueous sulfate electrolytes for rechargeable aqueous metal-ion batteries, our gum electrolyte would also be applicable for boosting the practical application of such batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...