Highly efficient and ultra-stable boron-doped graphite felt electrodes for vanadium redox flow batteries†
Abstract
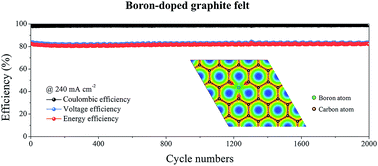
Developing high-performance electrodes with high operating current densities and long-term cycling stability is crucial to the widespread application of vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs). In this work, boron-doped graphite felt electrodes are designed, fabricated and tested for VRFBs. The first-principles study first demonstrates that the boron-doped carbon surface possesses highly active and stabilized reaction sites. Based on this finding, boron-doped graphite felt electrodes are fabricated for VRFBs. Testing results show that the batteries with boron-doped graphite felt electrodes achieve energy efficiencies of 87.40% and 82.52% at the current densities of 160 and 240 mA cm−2, which are 15.63% and 19.50% higher than those with the original electrodes. In addition, the batteries can also be operated at high current densities of 320 and 400 mA cm−2 with energy efficiencies of 77.97% and 73.63%, which are among the highest performances in the open literature. More excitingly, the VRFBs with the boron-doped graphite felt electrodes exhibit excellent stability during long-term cycling tests. The batteries can be stably cycled for more than 2000 cycles at 240 mA cm−2 with ultra-low capacity and efficiency decay rates of only 0.028% and 0.0002% per cycle. In addition, after refreshing the electrolytes, the performances of the batteries are nearly recovered regardless of the inevitable decay of the membrane. All these results suggest that highly efficient and ultra-stable boron-doped graphite felts are promising electrodes for VRFBs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...