An ab initio study for probing iodization reactions on metallic anode surfaces of Li–I2 batteries†
Abstract
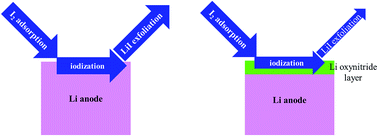
Lithium–iodine (Li–I2) batteries are considered a competitive candidate for next-generation electrochemical energy storage devices. The high solubility of I2 in aprotic solvents or aqueous solvent systems and the resulting shuttle effect can lead to the corrosion of metallic Li anodes. The present study employs atomistic scale modeling approaches to understand the interactions between Li surfaces and iodine species. It is found that the metallic Li (100) surface and Li (110) surface are very active to capture I2 molecules and facilitate the dissociation of these molecules. According to the ab initio molecular dynamics simulation, the iodization behavior is dependent on the coverage. When the iodine coverage is only 12.5%, the dissociated I atoms will not destroy the anode surface. As the coverage increases to 100%, a thin LiI layer forms but can be exfoliated from the Li surface, resulting in the irreversible loss of active materials. If the coverage is as high as 200%, a thick LiI film can form on the Li anode and deposit on the Li substrate. How the LiNO3 additive protects the Li–I2 battery anode is also studied in the present work. It is found that O and N atoms from the decomposition of the nitrate diffuse faster than I atoms in the metallic anode. Therefore, a Li oxynitride layer can form between the metallic Li metal and the iodine-containing species, which can cut off the direct interaction between the anode and I2 molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...