MOF-derived Zn–Mn mixed oxides@carbon hollow disks with robust hierarchical structure for high-performance lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
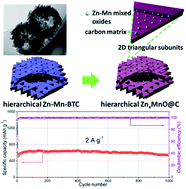
Hollow metal oxides and carbon hybrids with hierarchical and robust nanoarchitecture hold great potential as high-performance electrode materials. Herein, a relatively unexplored hollow and hierarchical metal–organic framework (MOF) assembled by parallel stacked triangular sub-MOFs were successfully synthesized via a facile co-precipitation method. The hollow MOFs were then converted to binary metal oxides@carbon composites, exemplified herein as Zn–Mn mixed oxides@carbon (ZnxMnO@C) hybrids. The obtained ZnxMnO@C inherits the unique hollow hexagonal nanodisks (HHNDs) structure of the MOF precursor, and each triangular plate-like subunit consists of a continuous carbon matrix embedded uniformly within the ultrafine ZnxMnO nanoparticles. When evaluated as an anode material for lithium ion batteries, the ZnxMnO@C HHNDs exhibited high specific capacity (1050 mA h g−1 at 0.1 A g−1 after 200 cycles) and remarkable cycling performance up to 1000 cycles. It is believed that besides the protection of the carbon matrix, the unique hierarchically hollow structure with parallel stacked subunits endows the ZnxMnO@C hybrid with additional capability to withstand lithiation/delithiation strain. Moreover, kinetics-analysis based on cyclic voltammograms (CVs) reveals that the high lithium storage capacity is primarily attributed to fast kinetics originating from pseudocapacitive contribution. This also accounts for the good rate capabilities of ZnxMnO@C HHNDs (713 and 330 mA h g−1 at 1 and 10 A g−1, respectively). Furthermore, full cells with Zn0.5MnO@C anodes and LiMn2O4 cathodes are assembled and show good cycling stability over 120 cycles. This study demonstrates a new hollow structure of MOFs and its usefulness in developing robust and hierarchical metal oxide/carbon composites for electrochemical storage applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...